The fundamental unit of life
Plasma membrane or Cell membrane

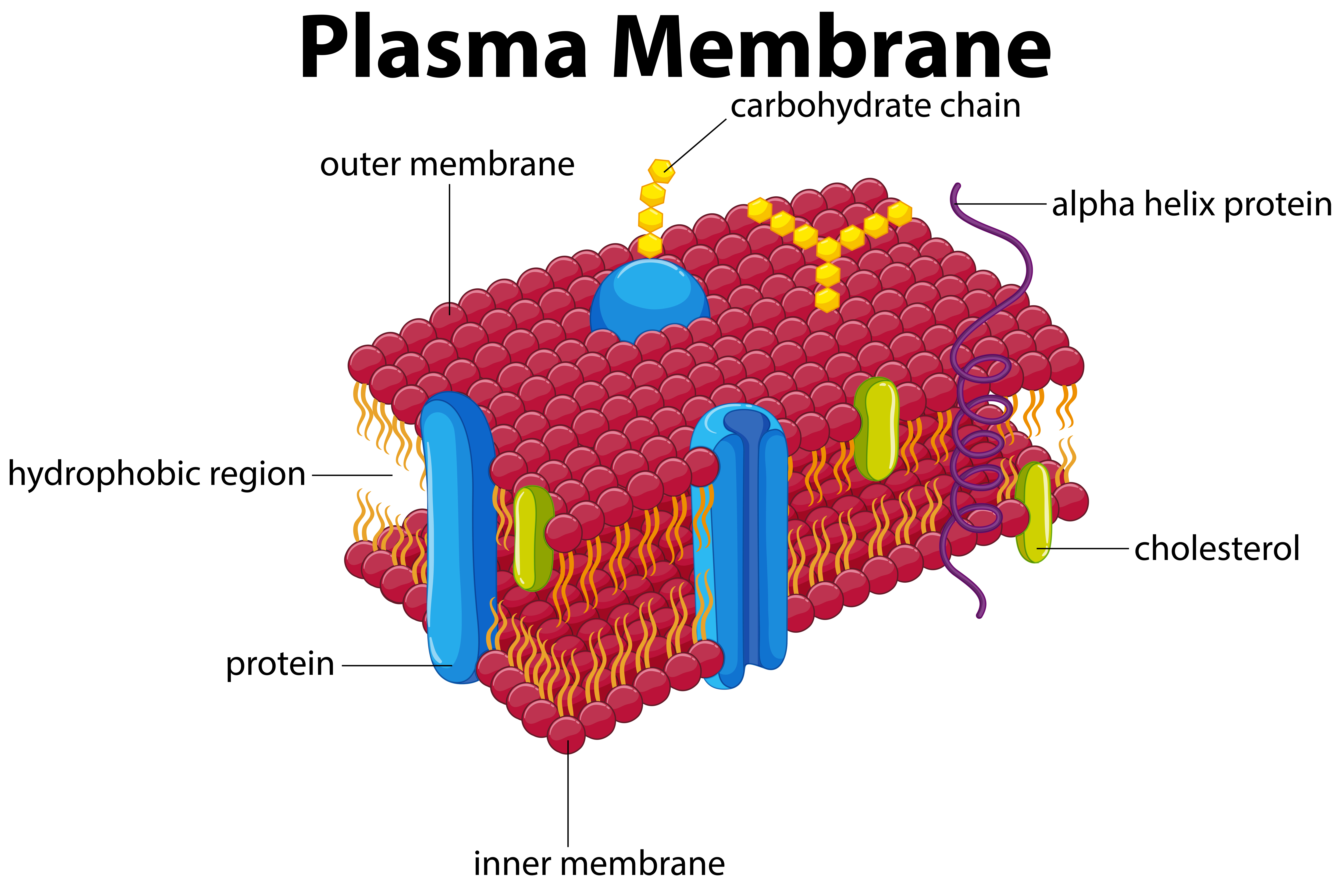
The plasma membrane of a cell is a network of lipids and proteins that forms the boundary between a cell’s contents and the outside of the cell. It is also simply called the cell membrane. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surrounding environment. It is semi-permeable and regulates the materials that enter and exit the cell. The cells of all living things have plasma membranes.
Functions of cell membrane:
- A Physical Barrier
- Selective Permeability
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis
- Cell Signaling
What will happen if we put an animal cell or a plant cell into a solution of sugar or salt in water?
- If the medium surrounding the cell has a higher water concentration than the cell, meaning that the outside solution is very dilute, the cell will gain water by osmosis. Such a solution is known as a hypotonic solution.
- If the medium has exactly the same water concentration as the cell, there will be no net movement of water across the cell membrane. Such a solution is known as an isotonic solution
- If the medium has a lower concentration of water than the cell, meaning that it is a very concentrated solution, the cell will lose water by osmosis. Such a solution is known as
a hypertonic solution..
Activity

- Remove the shell of an egg by dissolving it in dilute hydrochloric acid. The shell is mostly calcium carbonate. A thin outer skin now encloses the egg. Put the egg in pure water and observe after 5 minutes. What do we observe? The egg swells because water posses in it by osmosis.
- Place a similar de-shelled egg in a concentrated salt solution and observe for 5 minutes. The egg shrinks. Why? Water passes out of the egg solution into the salt solution because the salt solution is more concentrated.






