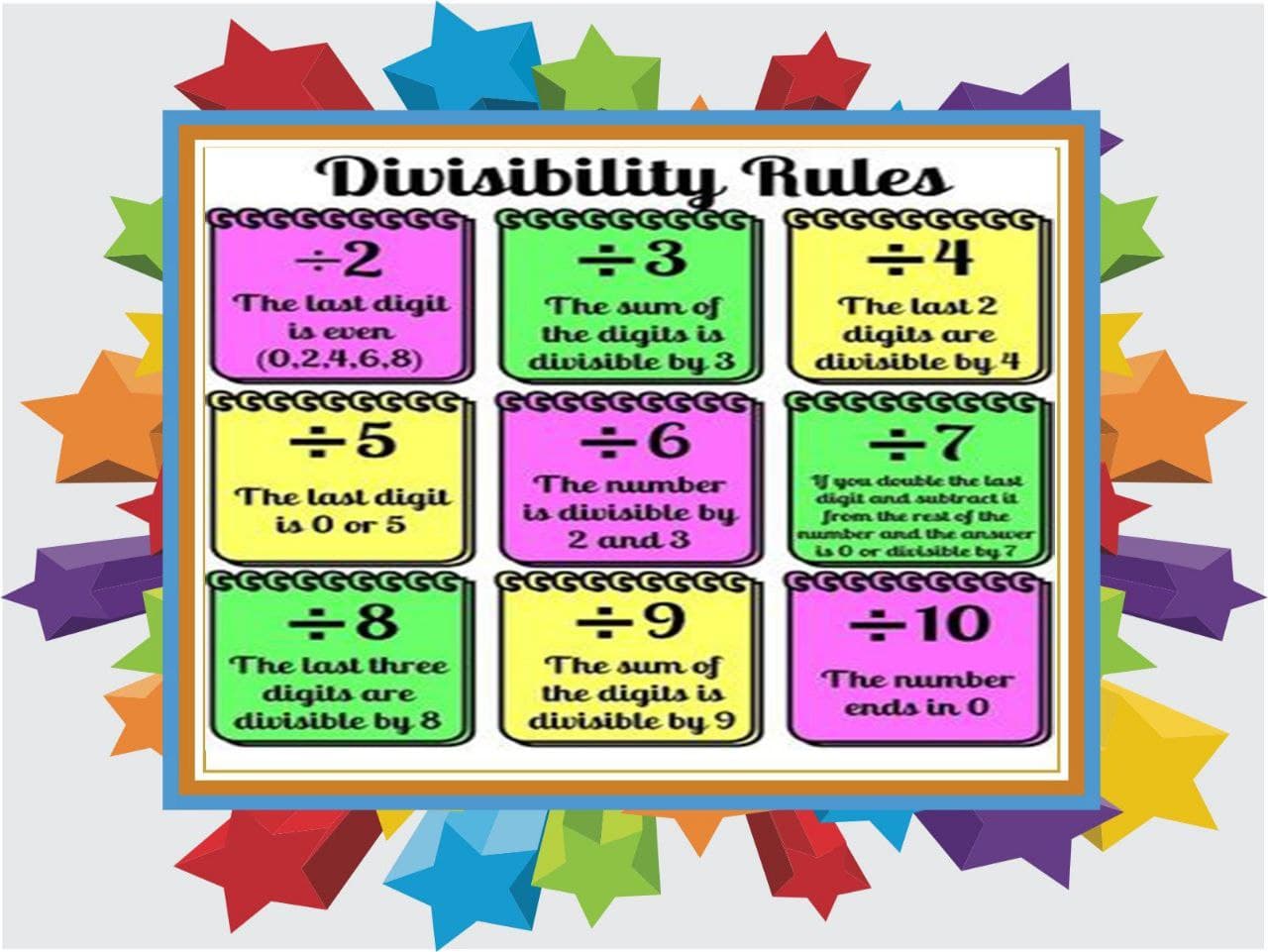
DIVISIBILITY RULES
Divisibility Rule of a number
The process of checking whether a number is divisible by a given number or not withoutactual division is called divisibility rule for that number.
For example, 15 divided by 3 is exactly 5 which implies that its remainder is zero. We then say that 15 is divisible by 3.
Divisibility by 2
A number is divisible by 2 if it has any of the digits 0,2,4,6 or 8 in it's ones place
Divisibility by 3
If the sum of the digits is a multiple of 3, then the number is divisible by 3.
Let us now add the digits of 21, 36, 54, 63, 72, 117
2 + 1 = 3
5 + 4 = 9
7 + 2 =9
3 + 6 = 9
6 + 3 = 9
1 + 1 + 7 = 9
All these sums are divisible by 3.
Divisibility by 5
A number is divisible by 5 if its units place is 0 or 5.
Divisibility by 6
If a number is divisible by both 2 and 3 then it is also divisible by 6.
270 is divisible by 2 because the last digit is 0. The sum of the digits is: 2 + 7 + 0 = 9 which is also divisible by 3. Therefore, 270 is divisible by 6.
Divisibility by 9
A number is divisible by 9, if the sum of the digits of the number is divisible by 9
we take 81, 8 + 1 = 9 similarly 99, 9 + 9 = 18 divisible by 9
Divisibility by 10
A number is divisible by 10 if it has zero (0) in its units place. All of them are divisible by both 5 and 2.
110, 200, 360, 490, 1190, 1510 here all these number is divisible by 10 because their units place is 0.
Divisibility by 11
A given number is divisible by 11, if the difference between the sum of the digits at odd places and the sum of the digits at even places (from the right) is either 0 or divisible by 11.