
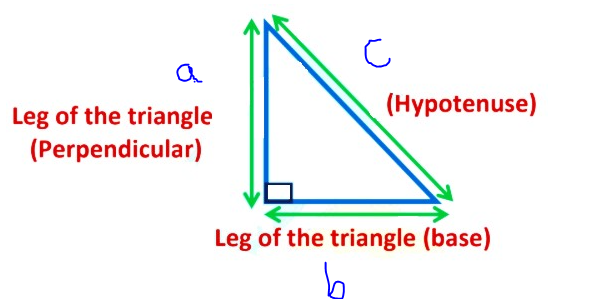
Pythagoras theorem states that “In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides“. The sides of this triangle have been named as Perpendicular, Base and Hypotenuse. Here, the hypotenuse is the longest side, as it is opposite to the angle 90°.
Consider the triangle given above:
Where “a” is the perpendicular,
“b” is the base,
“c” is the hypotenuse.
According to the definition, the Pythagoras Theorem formula is given as:
Hypotenuse2 = Perpendicular2 + Base2
c2 = a2 + b2
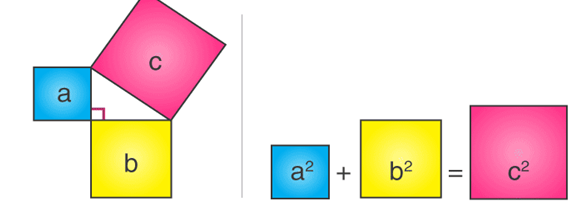
The side opposite to the right angle (90°) is the longest side (known as Hypotenuse) because the side opposite to the greatest angle is the longest
Consider three squares of sides a, b, c mounted on the three sides of a triangle having the same sides as shown.
By Pythagoras Theorem – Area of square “a” + Area of square “b” = Area of square “c”

The examples of theorem and based on the statement given for right triangles is given below:
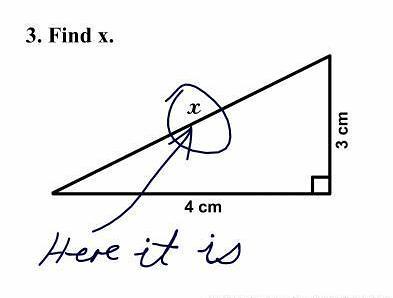
Consider a right triangle, given below.Find the value of x.
X is the side opposite to right angle, hence it is a hypotenuse.
Now, by the theorem we know;
Hypotenuse2 = Base2 + Perpendicular2
x 2= 82 + 62
x2 = 64+36 = 100
x = √100 = 10
Therefore, the value of x is 10.
Given the side of a square to be 4 cm. Find the length of the diagonal.
Given;
Sides of a square = 4 cm
To Find- The length of diagonal ac.
Consider triangle abc (or can also be acd)
(ab)2 +(bc)2 = (ac)2
(4)2 +(4)2 = (ac)2
16 + 16 = (ac)2
32 = (ac)2
(ac)2 = 32
ac = 4√2.
Thus, the length of the diagonal is 4√2 cm.