
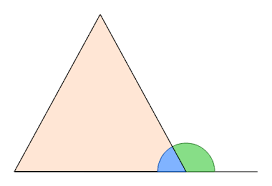
What is an exterior angle?
An exterior (or external) angle is the angle between one side of a triangle and the extension of an adjacent side.
The angle in green colour is Exterior angle.
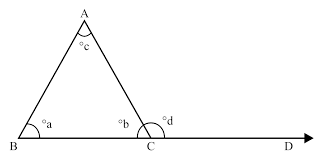
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles.
In the above figure exterior angle is d
According exterior angle property,d=a+c
Consider ∆ABC.
∠ACD is an exterior angle.
To Show: ∠ACD = ∠A + ∠B
Through C draw CE, parallel to BA
| S.no | Steps | Reasons |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ∠1 = ∠x | BA || CE and AC is a transversal. Therefore, alternate angles should be equal |
| 2. | ∠2 = ∠y | BA || CE and BD is a transversal. |
| 3. | ∠1 + ∠2 = ∠x + ∠y | From step-1 and step-2 |
| 4. | ∠1 + ∠2 = ∠x + ∠y | From the figure above. |
| 5. | ∠1 + ∠2 = ∠ACD | From step-3 and step-4 |
The above relation between an exterior angle and its two interior opposite angles is referred to as the Exterior Angle Property of a triangle.
The angle sum property of a triangle:The total measure of the three angles of a triangle is 180 °
From the above figure ,x+y+z=180 °
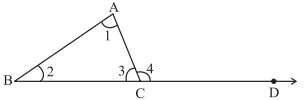
To justify this let us use the exterior angle property of a triangle. Given : ∠1, ∠2, ∠3 are angles of ΔABC. ∠4 is the exterior angle when BC is extended to D.
∠1 + ∠2 = ∠4 (by exterior angle property)
∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = ∠4 + ∠3 (adding ∠3 to both the sides).
But ∠4 and ∠3 form a linear pair so it is 180°.
Therefore, ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = 180.
Given that In a triangle, the two interior angles are 35 °and 60 ° are non adjacent to exterior angle x°. Find x.
Apply the Triangle exterior angle theorem:
that is, x °=35 °+60 °
x °=95 °
In the Δ ABC, x=55 °,y=55 ° , find the angle z °?
In Δ ABC,
x + y + z= 180 °
[By angle sum property of a triangle]
=> 55 ° + 55 ° + z °= 180 °
=> 110 ° + z ° = 180 °
=> z ° = 70 °