

* Agricultural practices encompass a wide range of activities and methods used to cultivate crops and raise livestock for food, fiber, and other products. These practices vary based on factors such as climate, soil type, available resources, and cultural traditions.
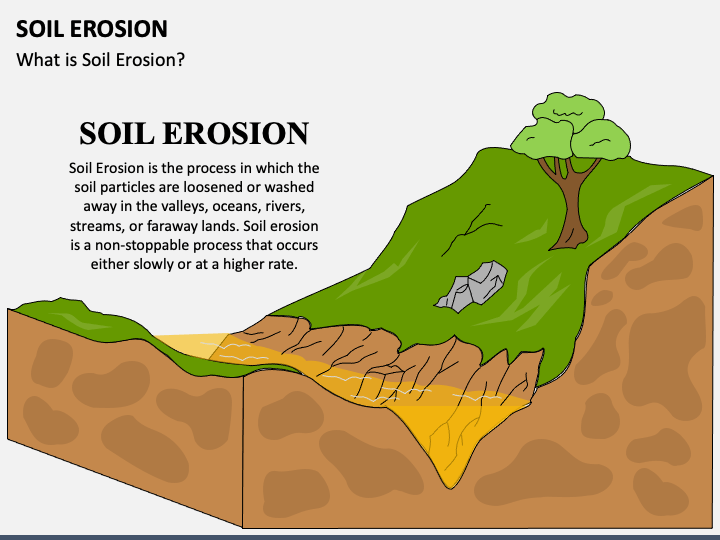
Soil erosion intensive farming practices, such as plowing and monoculture, can result in soil erosion, where topsoil is washed away by water or blown away by wind. Soil erosion reduces soil fertility, decreases agricultural productivity, and contributes to sedimentation in water bodies.
1. Water Pollution:- Runoff from agricultural fields can carry excess fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste into nearby water bodies, leading to water pollution.
2. Air Pollution: Agricultural practices can release greenhouse gases, such as methane and nitrous oxide, which contribute to global warming and climate change. Burning of crop residues and animal waste can also release particulate matter and other pollutants into the air.
3. Harm to Human Health: Pesticide residues in food and water can have adverse effects on human health, including an increased risk of cancer, reproductive issues, and neurological disorders.
4. Climate Change: Agricultural practices contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to global warming and climate change.
1.Precision Agriculture: Implementing precision agriculture techniques can optimize the use of fertilizers and pesticides. By using sensors, drones, and GPS technology, farmers can target specific areas that require treatment, reducing over-application and minimizing pollution.
2.Crop Rotation and Diversification: Rotating crops and diversifying planting can help prevent soil depletion and reduce the need for excessive fertilizers and pesticides. Different crops have different nutrient requirements and can naturally control pests, reducing chemical inputs.
3.Conservation Tillage: Adopting no-till or reduced tillage methods can help reduce soil erosion and nutrient runoff. Leaving crop residues on the field helps protect the soil, improve water infiltration, and sequester carbon.