BOHR'S ATOMIC THEORY :
Neils bohr proposed a model of an atom based on atomic spectra of hydrogen
He retained the basic concepts of Rutherford's model i.e., the atom has a positively charged nucleus at the center and the electrons revolve round the nucleus.He applied Planck's Quantum theory for revolving electron.
The main postulates are:
- Electrons revolvearound the nucleus with high velocity in circular paths called Orbit or shells.
- As long as the electron is in a particular orbit,its energy is constant.Therefore,these orbits are called stationary orbits
- Each stationary orbit is associated with a definite energy and is known as energy level.these energy levels are named as K,L,M,N,.... etc.,or numbered as 1,2,3,4,.... etc.
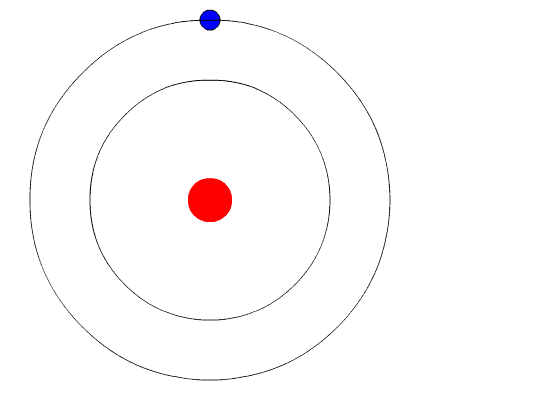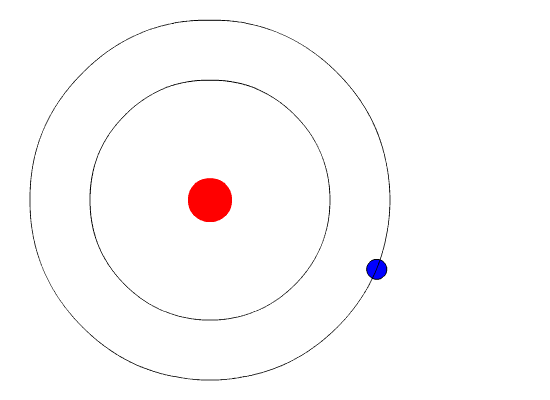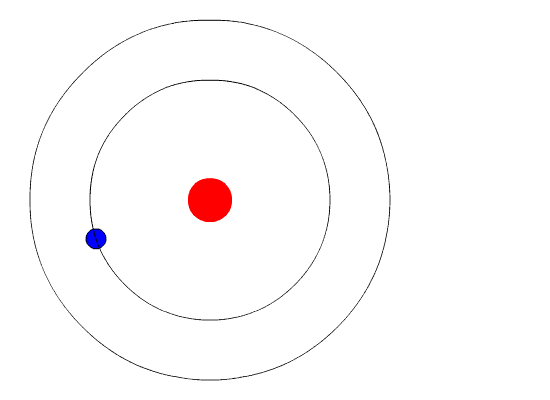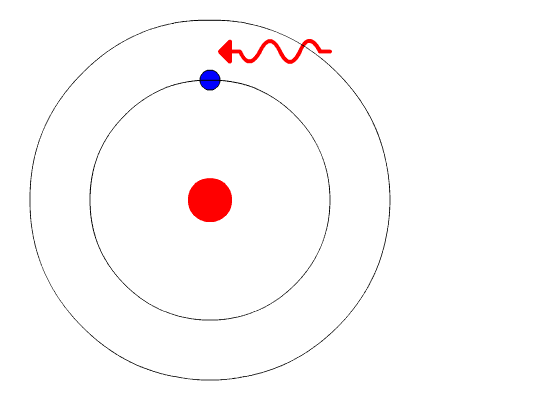
- When an electron jumps from a higher energy level to a lower energy level,the difference in energy is emitted as radiation in quanta.
When an electron jumps from a lower energy level to a higher energy level,the difference in energy is absorbed as radiation in quanta.
E2 - E1 = hu
where,
E1 = energy of first orbit
E2 = energy of second orbit
h = Planck's constant (6.625 * 10-34) J.sec
u = frequency of radiation
- The angular momentum of the electron revolving in a stationary orbit is equal to integral multiples of h/(2*pI).
Angular momentum,
mvr = nh/(2*PI)
Where,
m =mass of electron
v = velocity of electron
r = radius of orbit
n = integer (1,2,3,4,....)
h = Plank's constant